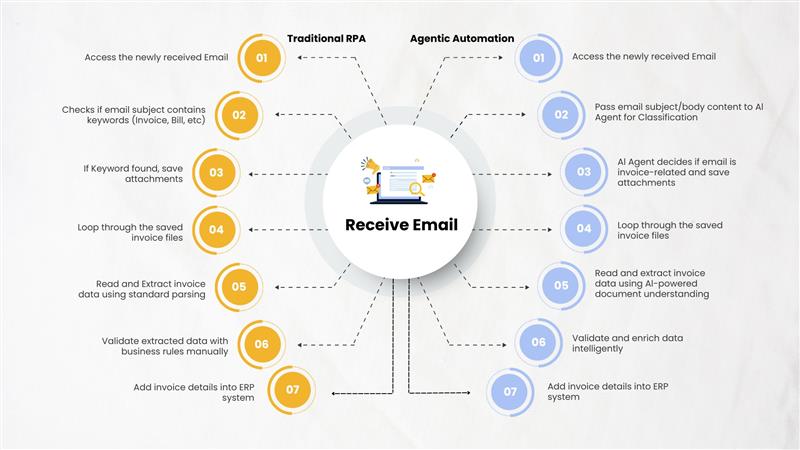
Traditional RPA
RPA uses software “robots” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human interactions with digital systems (like clicking buttons or entering data)
Key Characteristics
Key Characteristics
- Rule-Based:Operates based on predefined rules and scripts.
- Deterministic:Outcomes are predictable and consistent.
- UI-Centric:Interacts with applications through the user interface.
- Low Intelligence:Limited decision-making; cannot adapt to changes easily.
- Static Workflows:Tasks are rigid and need reprogramming for changes.
- Requires Human Supervision:Cannot function autonomously beyond scripted tasks.

Example Use Cases
- Data entry from emails to spreadsheets
- Invoice processing
- Copy-pasting between systems
- Web scraping

Agentic Automation
Agentic automation involves AI-driven agents capable of goal-oriented behaviour. These agents can plan, reason, adapt, and act autonomously in dynamic environments to achieve objectives.
Key Characteristics:
Key Characteristics:
- Goal-Based:Agents work towards outcomes, not just following steps.
- Autonomous:Can operate with minimal human input.
- Adaptive: Learns from the environment and can handle variability.
- Cognitive Abilities: Incorporates NLP, reasoning, and sometimes learning (LLMs, multi-agent systems).
- Dynamic Workflows: Can adjust steps in real time based on context or results.
- High-Level Orchestration:Capable of coordinating across systems and tasks.
Example Use Cases
- Multi-agent screens resume to find top candidates
- Agent Scraps data from email for an invoice
- Clipboard AI auto-fills fields